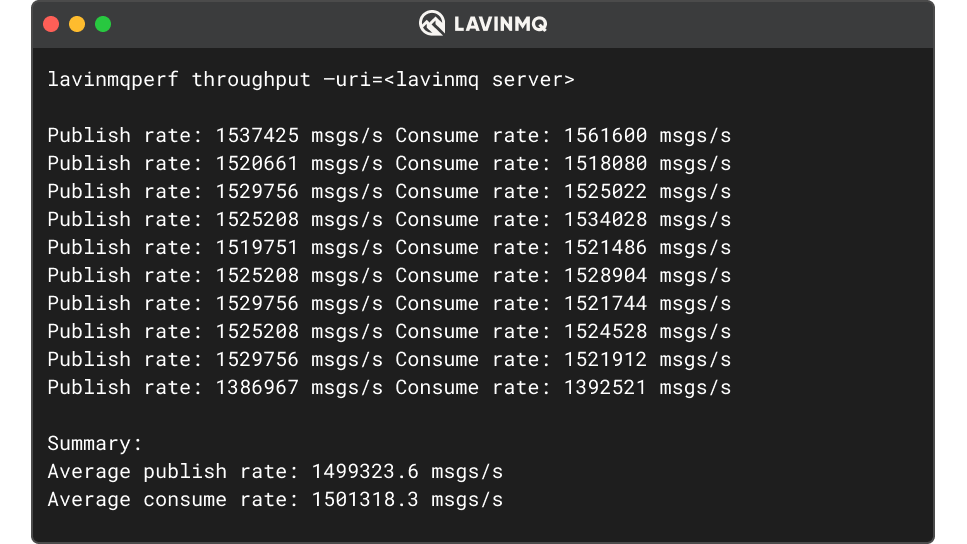
 84codes
LavinMQ: Understanding code to get the best performance
84codes
LavinMQ: Understanding code to get the best performance
News
Become a Crystal sponsor in only 3 simple steps via OpenCollective
ContributeYou can tap into the expertise of the very creators of the language to guide you in your implementation.
Hire UsTop Sponsors
Success stories
Section titled Success stories 84codes
LavinMQ: Understanding code to get the best performance
84codes
LavinMQ: Understanding code to get the best performance
 Bright Security
Crystal: the lingua franca at Bright
Bright Security
Crystal: the lingua franca at Bright
 PlaceOS
Automating smart buildings with Crystal
PlaceOS
Automating smart buildings with Crystal



 84codes
84codes
